Reaction Time Test: Measure Your Reaction Speed & Improve Your Performance
September 7, 2025 | By Marcus Adler
Ever wondered what "reaction time" truly means and why it's so important? From dodging an obstacle while driving to landing a critical hit in a video game, your reaction speed is a key performance indicator in daily life. This guide will demystify the various reaction time test types, explore their real-world applications, and help you understand what your score signifies. What is a good reaction time? By the end of this article, you'll not only know the answer but also have the perfect tool to find yours. Ready to begin? You can discover your results right now.

Types of Reaction Time Tests: Beyond the Click Test
While you might be familiar with a basic click test, the world of reaction time measurement is far more diverse. Different tests are designed to measure specific aspects of our cognitive and neural processing. Understanding these variations helps you appreciate the complexity behind a seemingly simple reflex.
Simple Reaction Time: Measuring Pure Speed
This is the most fundamental type of test. It involves a single, predictable stimulus and requires a single, predetermined response. Think of a sprinter starting a race at the sound of the gun. The goal is to measure the raw processing speed of your nervous system—how quickly a signal can travel from your eyes or ears to your brain and then to your muscles. The tool on our homepage is a classic example of a simple reaction test that precisely measures this core reflex.
Choice Reaction Time: When Decisions Matter
Life is rarely about responding to one predictable signal. Choice reaction time (CRT) tests introduce complexity by presenting multiple possible stimuli, each requiring a different response. For example, a test might flash a red or blue light, and you must click the left mouse button for red and the right for blue. This measures not just your raw speed but also your decision-making speed, a critical cognitive function for everything from complex gaming to navigating busy intersections.

Discrimination & Go/No-Go Tests: Focus and Inhibition
These tests measure your ability to differentiate between stimuli and withhold a response when necessary. In a Go/No-Go test, you might be instructed to click for every green square (Go) but not for any red squares (No-Go). This assesses your inhibitory control and attention, key components of focus and inhibition. It's a skill that prevents you from swinging at a bad pitch in baseball or making impulsive decisions.
Auditory vs. Visual Reaction Time: Which Stimulus is Faster?
Have you ever wondered if you react faster to what you hear or what you see? The answer is generally what you hear. The neural pathway for auditory visual reaction processing is shorter than for visual stimuli. Auditory signals reach the brain in about 8-10 milliseconds, while visual signals take 20-40 milliseconds. This difference, though tiny, can be the margin between winning and losing for a professional gamer or athlete.
Real-World Applications of Reaction Time
Measuring your reaction time is more than just a fun exercise; it’s a quantifiable metric with significant implications across various fields. From the esports arena to the doctor's office, this simple number tells a powerful story about performance and well-being.
Enhancing Performance in Sports & Athletics
For athletes, milliseconds matter. A boxer's ability to dodge a punch, a tennis player's return of a 120 mph serve, or a race car driver's start off the line are all heavily dependent on elite reaction time. Coaches and trainers use reflex training drills and reaction tests to monitor an athlete's physical and mental readiness, tracking their performance and identifying areas for improvement in their sports anticipation skills.
Boosting Your Edge in Competitive Gaming
In the world of competitive gaming, a fast reaction time is non-negotiable. Whether it's an FPS player landing a headshot or a MOBA player dodging a skill shot, superior reflexes define top-tier competitors. Gamers use tools like our reaction time game to benchmark their skills, warm up before matches, and track improvement over time. Understanding your reaction speed can even inform decisions about optimizing your gaming gear for lower latency.

Cognitive Health, Driving Safety & Everyday Life
Beyond competitive arenas, reaction time is a vital indicator of cognitive health. Neurologists may use reaction time tests to assess brain function and monitor the progression of certain neurological conditions. For the average person, it has direct safety implications, particularly in driving, where a split-second delay can be the difference between a near-miss and an accident. Regularly checking your score with a reflex test can be a simple way to stay mindful of your cognitive sharpness.
Understanding & Interpreting Your Reaction Time Score
You’ve taken the test, and a number in milliseconds (ms) is on your screen. But what does it mean? Interpreting your score requires context, including benchmarks, averages, and an understanding of the many factors that can influence it.
What is a Good Reaction Time? Benchmarks & Averages
While there's no single "perfect" score, we can look at averages to establish benchmarks. For a simple visual reaction test, the average reaction time for most people is around 200-270 milliseconds. Highly trained individuals, like fighter pilots or professional gamers, often score between 150-180 ms. Anything under 200 ms is considered excellent, while scores over 300 ms may indicate room for improvement. The best way to understand your standing is to check your score multiple times and find your personal average.
Factors Influencing Your Reaction Time Results
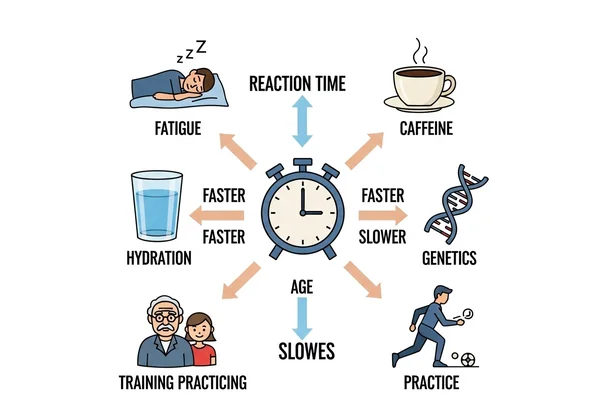
Your score isn't static; it can fluctuate based on numerous variables. Age is a significant factor, with reaction time typically peaking in your early 20s and gradually slowing thereafter. Other key influences include:
-
Sleep: Fatigue dramatically slows reaction speed.
-
Caffeine: This stimulant can temporarily shorten reaction time.
-
Hydration: Dehydration has been shown to impair cognitive performance.
-
Genetics: Is reaction time genetic? To some extent, yes. Your genetic makeup can set a baseline for your neural processing speed.
-
Practice: Like any skill, you can improve reaction time with consistent training.
Acknowledging Online Test Limitations
It's crucial to approach any online test with an understanding of its limitations. While our tool is designed for accuracy, external factors like hardware latency can affect the absolute score. Your monitor's refresh rate (FPS), your mouse's polling rate, and even your internet connection can add a few milliseconds of delay. Therefore, it's best to use online tests as a consistent tool for personal tracking and improvement rather than comparing your scores to lab-grade scientific data.
Your Journey to Faster Reflexes Starts Here
Understanding the different types of reaction time tests, their real-world importance, and how to interpret your score empowers you to take control of your cognitive performance. Whether you're a gamer seeking a competitive edge, an athlete striving for peak performance, or simply someone interested in maintaining your mental sharpness, measuring and training your reflexes is a proactive step forward.
The knowledge you've gained is the first step. The next is to put it into practice. Establish your baseline, track your progress, and challenge yourself to improve. Your journey to faster reflexes begins with a single click. Take the test now and see where you stand!
Frequently Asked Questions About Reaction Time Tests
What is considered a good reaction time?
A score between 200-270 milliseconds is considered average for a simple visual reaction time test. Scores under 200 ms are excellent and often seen in highly trained individuals. The key is to establish your personal average and work on improving it with a reliable reaction time trainer.
What is the fastest human reaction time ever recorded?
While difficult to verify outside of a lab, the theoretical limit for human visual reaction time is believed to be around 100 milliseconds. Some professional athletes and gamers have reported scores in the 120-150 ms range, which represents the absolute peak of human performance.
Does my gaming setup (like FPS) affect my reaction time test score?
Yes, absolutely. A monitor with a higher refresh rate (Hz/FPS) displays the stimulus faster, and a mouse with a higher polling rate sends your click signal to the computer more quickly. This hardware latency can add 10-30 ms or more of delay, which is why a consistent setup is key for accurate personal tracking.
What are common causes for a slow reaction time?
Several factors can lead to a slower reaction time. The most common causes include fatigue, dehydration, stress, and lack of focus. Age is also a natural factor. If you notice a sudden and significant decline in your reaction speed, it is always best to consult with a healthcare professional.