Reaction Time & Driving Safety: The Crucial Link
June 15, 2025 | By Marcus Adler
When you're behind the wheel, every second—every millisecond—can make a life-or-death difference. Many drivers wonder, A driver's reaction time may affect what distance? The answer is critical for driving safety. Understanding the link between reaction time driving and your ability to respond to hazards is paramount for responsible road use. While our site offers a general online reaction test using color changes, this article explores how your inherent reaction capabilities play a vital role in preventing accidents.
Understanding Driver Reaction Time: More Than Just Speed
What exactly is driver reaction time? It's not just about how fast you can physically move, but how quickly your brain processes information and initiates a response.
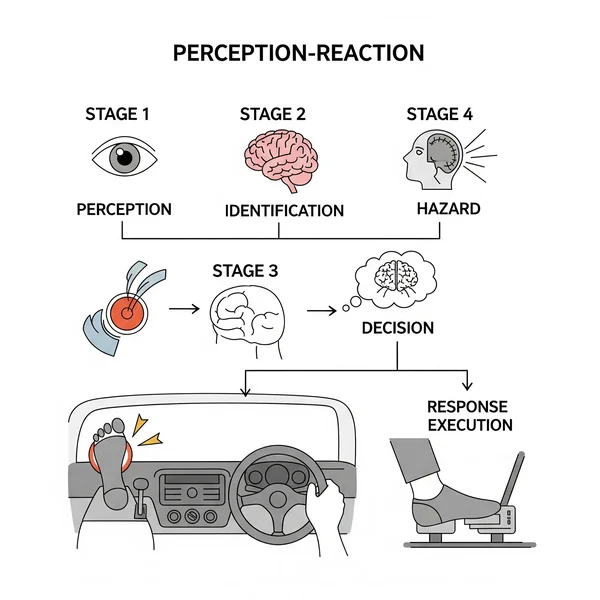
The Perception-Reaction Process in Driving
Perception-reaction time (PRT) in driving involves several stages:
-
Perception: Seeing or hearing a hazard (e.g., a car suddenly braking, a pedestrian stepping out).
-
Identification: Recognizing it as a hazard.
-
Decision: Deciding on an action (e.g., brake, steer).
-
Response Execution: Physically performing the action. This entire sequence contributes to your overall
driver reaction time.
What is an Average Driver Reaction Time?
The average driver reaction time typically falls between 0.75 to 1.5 seconds. However, this can vary significantly based on numerous factors affecting driver reaction time. It's important to remember that this is just an average, and individual capabilities can differ. Curious about your general visual reaction? Test your reaction speed here.
The Critical Impact of Reaction Time on Driving Safety
A delayed reaction, even by a fraction of a second, can drastically alter the outcome of a critical driving situation. This is where understanding reaction distance becomes crucial for driving safety.
Reaction Distance: The Unseen Part of Stopping (Calculating Reaction Distance)
A driver's reaction time may affect what distance? It directly affects the reaction distance – the distance your vehicle travels from the moment you perceive a hazard until you physically begin to apply the brakes or take evasive action.
How Your Reaction Time Affects Braking Distance
The total stopping distance of a vehicle is a combination of this reaction distance and the actual braking distance (the distance traveled while the brakes are applied). A longer driver reaction time means a longer reaction distance, significantly increasing the total space needed to stop safely. For example, at 60 mph (approx 88 feet per second), a 1-second reaction time means you travel 88 feet before you even start braking.
Real-World Scenarios: Why Reaction Distance Matters
Consider emergency situations: a child darting into the road, or the car ahead slamming on its brakes. In these moments, your perception-reaction time dictates whether you can avoid a collision. Even a half-second improvement in driver reaction time can mean the difference between a near miss and a serious accident.
Common Factors Affecting Driver Reaction Time (Influences on Driving Reaction Speed)
What factors influence driver reaction? Many things can impair your reaction time driving:
-
Distractions: Texting, calls, adjusting the radio, or even engaging in deep conversation are major culprits.
Alert drivingmeans minimizing all distractions. -
Fatigue and Drowsiness: Driving tired can be as dangerous as
impaired drivingunder the influence. Yourreaction speedplummets when fatigued. -
Alcohol, Drugs, and Medications: These substances severely impair judgment, coordination, and
driver reaction time. There's no safe level of impairment when driving. -
Age and Experience: While older drivers might experience some natural slowing of reflexes, experience can sometimes compensate through better
hazard perceptionanddefensive drivingskills. Younger, less experienced drivers might have quicker raw reactions but lack judgment. -
Weather and Road Conditions: Rain, snow, fog, or poor road surfaces can increase the time needed to perceive and react to hazards, impacting
driving safety.
Consequences of Slow Reaction Time While Driving (Dangers of Delayed Driver Response)
A compromised driver reaction time leads to:
- Increased Risk of Collisions: Especially rear-end collisions and intersection accidents where quick responses are vital.
- Inability to Avoid Hazards: Less time to react to pedestrians, animals, debris on the road, or sudden stops by other vehicles. This directly impacts overall
road safety.
How to Improve Reaction Time for Safer Driving
While you can't change your base physiological reaction speed overnight, you can adopt safe driving habits and strategies to maximize your responsiveness and improve driving reaction effectiveness. How to improve reaction time for driving?
Practicing Defensive Driving Techniques
Defensive driving involves anticipating potential hazards before they fully materialize. This means scanning ahead, maintaining a safe following distance, and being aware of your surroundings, effectively giving you more time for hazard perception and reaction.
Minimizing Distractions: Staying Focused on the Road
Create a distraction-free zone in your car. Put your phone away or on silent, set your GPS before you start, and avoid activities that take your eyes or mind off the task of alert driving.

Ensuring Adequate Rest Before Driving
Never drive when you're tired. Prioritize getting enough sleep before any journey, especially long ones. This is crucial for maintaining optimal reaction time driving.
Understanding Your Own Limitations
Be honest with yourself about your current state. If you're feeling unwell, stressed, or are on medication that might affect your alertness, consider alternative transportation. Responsible driving includes knowing when not to drive.
Can You Test Your Driving-Related Reaction Time?
While online tests like ours at ReactionTimeTest.net (which measures your response to a color change) aren't driving simulators, they can help increase your awareness of how quickly you generally react to visual stimuli. This self-awareness can encourage safer driving practices.
Your Reaction Time, Your Responsibility for Road Safety
Your driver reaction time is a critical component of driving safety. While many factors affecting driver reaction time exist, adopting safe driving habits, staying alert, and understanding the concept of reaction distance can significantly reduce your risk on the road. It's every driver's responsibility to ensure they are fit and focused, contributing to overall road safety for everyone.
How do you ensure you maintain alert driving and quick reactions on the road? Share your tips for driving safety in the comments below!
Your Reaction Time Questions Answered
-
What is the average reaction time for a driver?
The
average driver reaction timeis generally considered to be between 0.75 and 1.5 seconds. However, this can be influenced by manyfactors affecting driver reaction timesuch as age, fatigue, and distractions. -
A driver's reaction time may affect what distance?
A driver's
reaction timedirectly affects thereaction distance– the distance the vehicle travels from the moment a hazard is perceived until the driver initiates a physical response (like braking). This is a key component of the totalstopping distance. -
How to improve reaction time for driving?
While you can't drastically change your base neural processing speed, you can
improve driving reactioneffectiveness by practicingdefensive driving, minimizing distractions, ensuring you're well-rested, and avoiding impairments. Being aware of your general reaction capabilities through tools like our online reaction speed test can also promote safer habits. -
Can I test my driving reaction time?
Specific driving simulators can assess driving-related reactions. General
reaction time testtools, such as the visual cue test on our site, ReactionTimeTest.net, can give you an idea of your baseline visual reaction speed, which is a component ofdriver reaction time. This can help build awareness fordriving safety. -
What factors influence driver reaction?
Key
factors affecting driver reaction timeinclude distractions (e.g., phone use), fatigue, alcohol or drug impairment, age, experience, and even weather conditions. Maintainingalert drivingis crucial for optimalreaction time driving.